Monocular 3D Human Mesh Recovery
(a.k.a. 3D human pose and shape estimation) in the deep learning era
主要考虑RGB图片和单目RGB视频(统称为monocular images)作为输入
存在问题
- 将2D观察提升到3D空间存在固有的模糊性
- 多变的人体运动结构
- 与环境复杂的交互
两种范式:
- 基于优化:以迭代方式显式地将身体模型拟合到2D观察结果,各种数据项和正则化项被探索作为优化目标。
- 基于回归:利用神经网络强大的非线性映射能力,直接从原始图像像素预测模型参数。
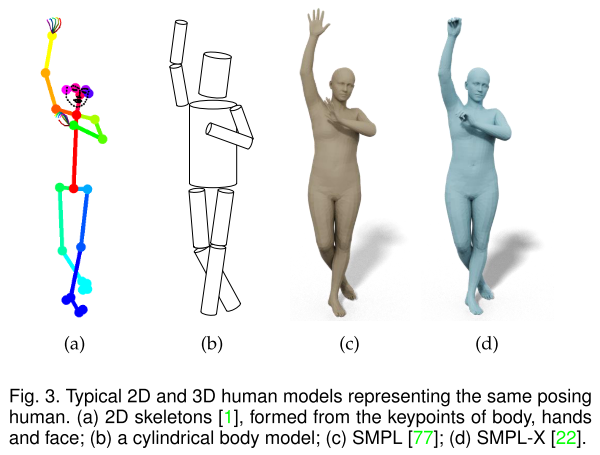
Human Modeling
基于骨架:无法获得人体的表面
基于几何图元(geometric primitives,包括平面矩形,圆柱等):人体模型是手工制作的,不符合实际
statistical modeling:为了将密集点云和三角网格从3D扫描转换为水密的(watertight)和可动画(animatable)的3D人体网格,采取三个主要的预处理步骤:
template mesh registration: fit a template mesh to the 3D point cloud to deal with holes that the triangulated
mesh contains模板网格配准
skeleton fitting: determine the number of joints and the location and axis orientations of rotations for each joint
骨架匹配:确定关节的数量以及每个关节的旋转位置和轴方向
skinning: bind every vertex in the surface to the skeleton for animation
蒙皮:将曲面中的每个顶点绑定到骨骼以进行动画