OpenScene
CVPR 2023 OpenScene: 3D Scene Understanding with Open Vocabularies
https://pengsongyou.github.io/openscene
在复杂的3D场景中识别对象、材料、可利用性、活动和房间类型,所有这些都使用同一个模型进行训练,而不需要任何标记的3D数据,引入了开放词汇3D场景理解任务,arbitrary text queries are used for semantic segmentation, affordance estimation, room type classification, 3D object search, and 3D scene exploration
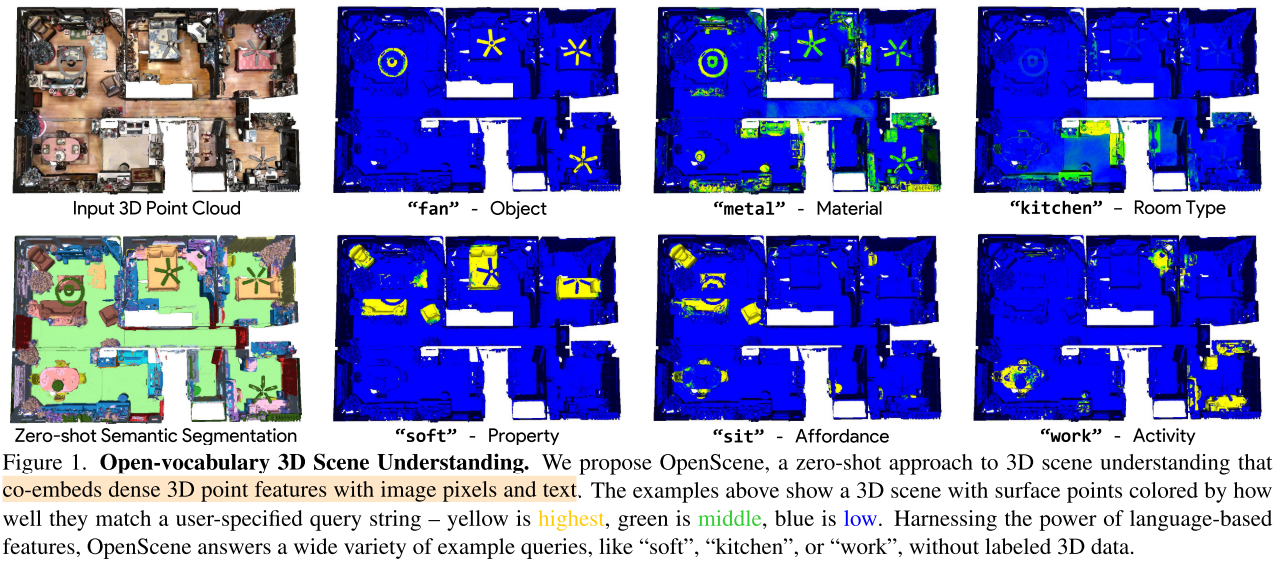
Motivation
给定一个带有一组位姿以及RGB信息的三维网格或点云,目标是推断每个三维点的语义、可利用性、功能和物理特性
Given a 3D mesh or point cloud with a set of posed RGB images, the goal is to infer the semantics, affordances, functions, and physical properties of every 3D point
例如,在上图中所示的房子中,我们想要预测哪些表面是风扇的一部分(语义)、由金属制成(材料)、在厨房内(房间类型)、一个人可以坐的地方(可利用性)、一个人可以工作的地方(功能),以及哪些表面是软的(物理特性)。
Answers to these queries can help a robot interact intelligently with the scene or help a person understand it through interactive query and visualization.
挑战:
- 传统的3D场景理解模型通过针对特定任务设计的基准数据集的监督训练而得到的(例如,针对20个类别的封闭集合的3D语义分割)。它们每个都设计用于回答一种类型的查询(这个点是在椅子、桌子还是床上吗?),但对于训练数据稀缺的相关查询(例如,分割罕见的物体)或没有3D监督的其他查询(例如,估计材料特性),提供的帮助很少
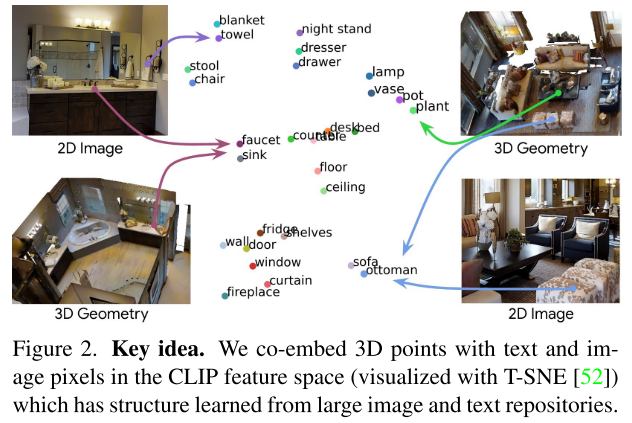
Key idea
compute dense features for 3D points that are co-embedded with text strings and image pixels in the CLIP feature space
为了实现这一目标,作者建立了3D场景中的3D点与位姿图像中的像素之间的关联,并训练一个3D网络,使用CLIP像素特征作为监督来编码3D点。这种方法将3D点与特征空间中的像素对齐,进而与文本特征对齐,从而实现对3D点的开放词汇查询。
Related Work
- Closed-set 3D Scene Understanding
- Open-Vocabulary 2D Scene Understanding
- Zero-shot Learning for 3D Point Clouds
Methodology
- 使用一个预训练的面向开放词汇的2D语义分割模型为每个图像计算每个像素的特征,多视图的像素特征聚合到每个3D点上,形成每个点的融合特征向量(Image Feature Fusion)
- 使用仅接受3D点云(只有坐标)作为输入的3D网络来提炼出这些融合特征(3D Distillation),从3D点云几何形状中进行特征提取,并使用最小化与聚合像素特征之间差异的损失
- 将2D融合和3D网络产生的特征组合成每个3D点的特征(2D-3D Feature Ensemble),并使用它来回答开放词汇的查询(Inference)
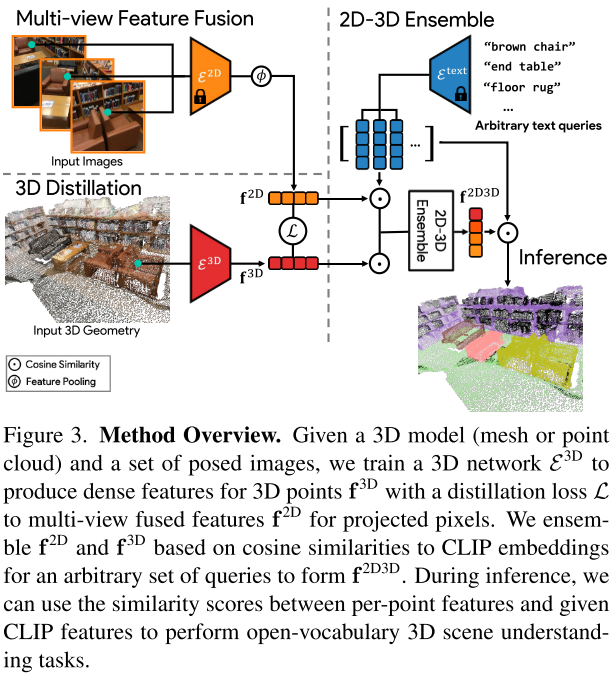
Image Feature Fusion
利用2D视觉语言分割模型(作者实验了OpenSeg和LSeg)提取每个RGB图像的密集像素级Embeddings,然后将它们反投影到场景的3D表面点上。使用average pooling来融合多视角特征。
3D Distillation
当存在图像时,特征点云$\mathbf{F}^{2 \mathrm{D}}=\left\{\mathbf{f}_{1}^{2 \mathrm{D}}, \cdots, \mathbf{f}_{M}^{2 \mathrm{D}}\right\} \in \mathbb{R}^{M \times C}$可以直接用于基于语言的3D场景理解。然而,这样融合的特征可能会导致嘈杂的分割,因为2D预测可能是不一致的。此外,有些任务只提供3D点云或网格。因此,作者提出将这种2D视觉语言知识提炼到一个只接受3D点位置作为输入的3D点网络中。
使用MinkowskiNet18A作为3D backbone
最大化$\mathbf{F}^{2 \mathrm{D}}$和$\mathbf{F}^{3 \mathrm{D}}$的余弦相似度
$\mathcal{L}=1-cos(\mathbf{F}^{2 \mathrm{D}},\mathbf{F}^{3 \mathrm{D}})$
2D-3D Feature Ensemble
作者仍然提出了一种2D-3D集成方法,用来获得混合特征以提高性能。作者观察到:2D融合特征更擅长预测小物体(例如桌子上的杯子)或几何不确定的物体(例如墙上的画),而3D特征则对具有独特形状的物体(例如墙壁和地板)具有良好的预测效果。作者的目标是将两者的优点结合起来。作者提出的集成方法利用一组文本提示,在推理或离线时提供(例如来自ScanNet等公共基准测试中预定义的类别,或由用户定义的任意类别)。
使用CLIP文本编码器提取所有文本提示的embeddings,然后计算文本embeddings和2D融合特征/3D Distillation特征的余弦相似度,将最大值作为对应特征的集成分数。
Experiment
Datasets:
- ScanNet
- Matterport3D
- nuScenes Lidarseg
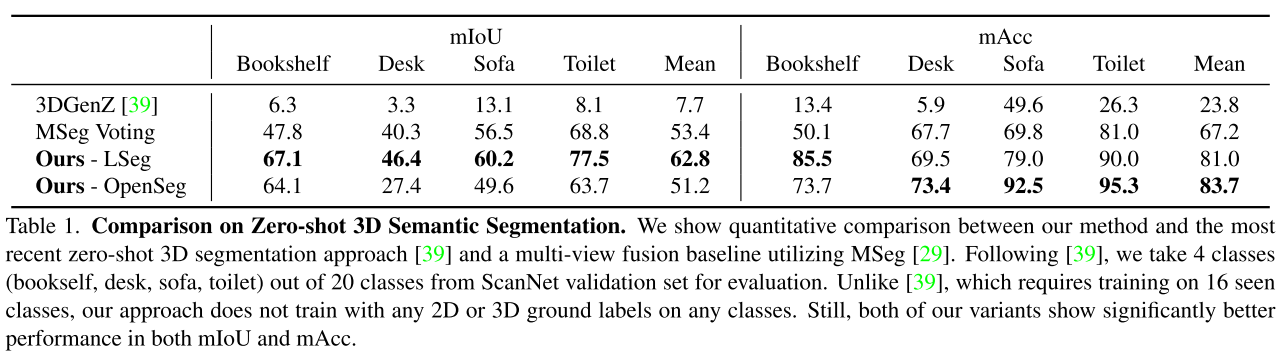
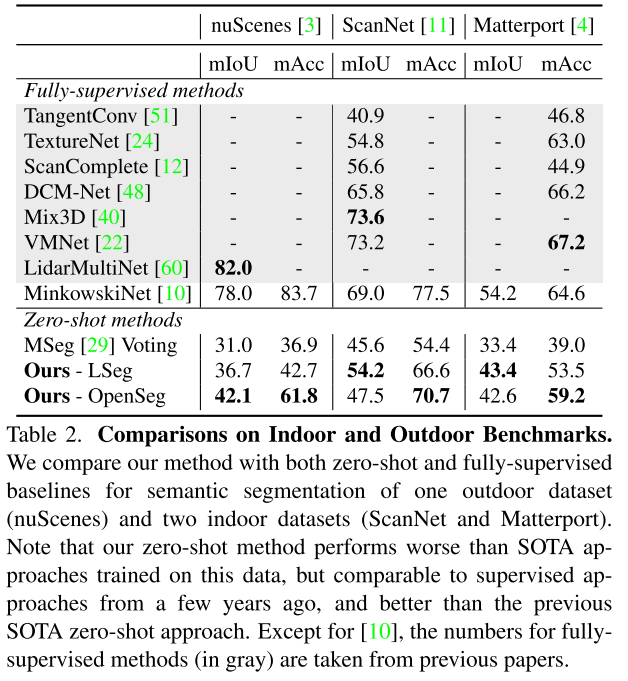
Comparison on zero-shot 3D semantic segmentation
主要对比的工作:
- MSeg Voting
- 3DGenz
- divides the 20 classes of the ScanNet dataset into 16 seen and 4 unseen classes, and trains a network utilizing the ground truth supervision on the seen classes to generate features for both sets.
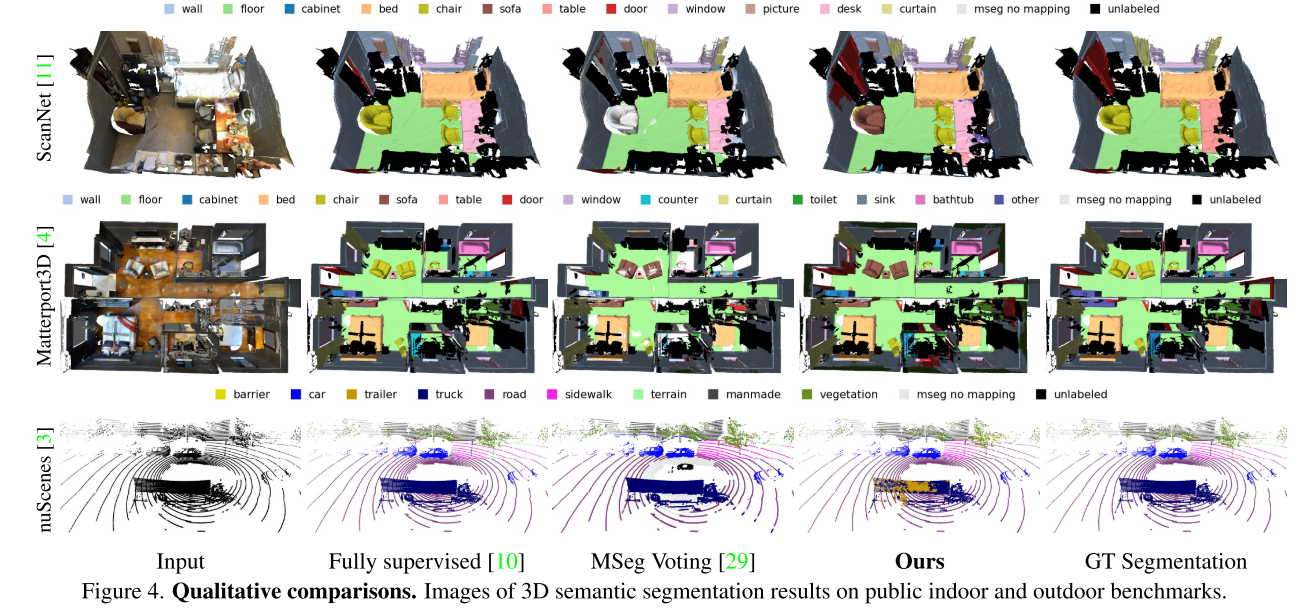
Comparison on 3D semantic segmentation benchmarks
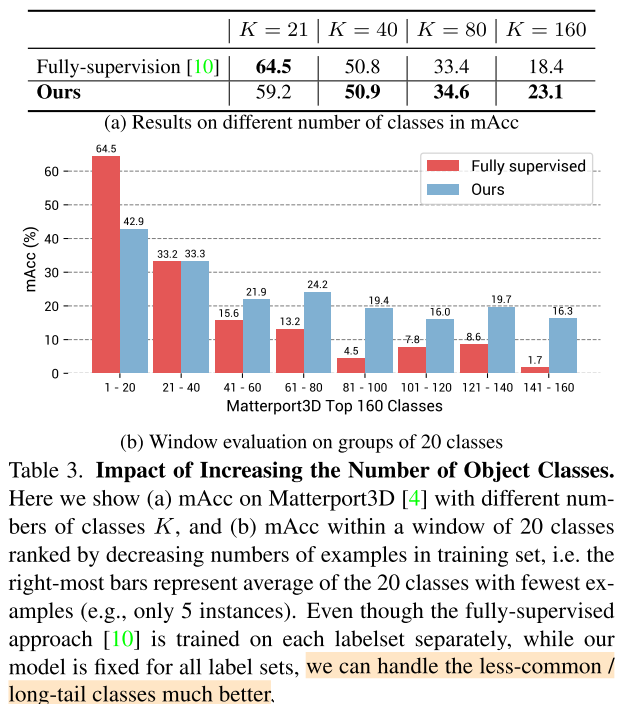
Impact of Increasing the Number of Object Classes
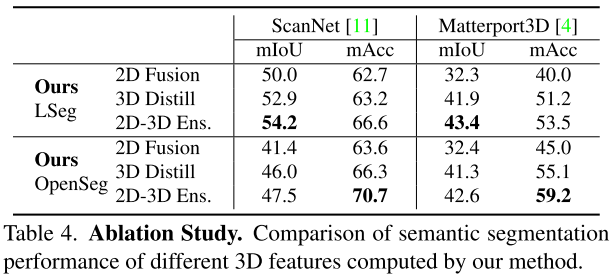
Ablation Studies
OpensSeg准确率和泛化性比LSeg更好
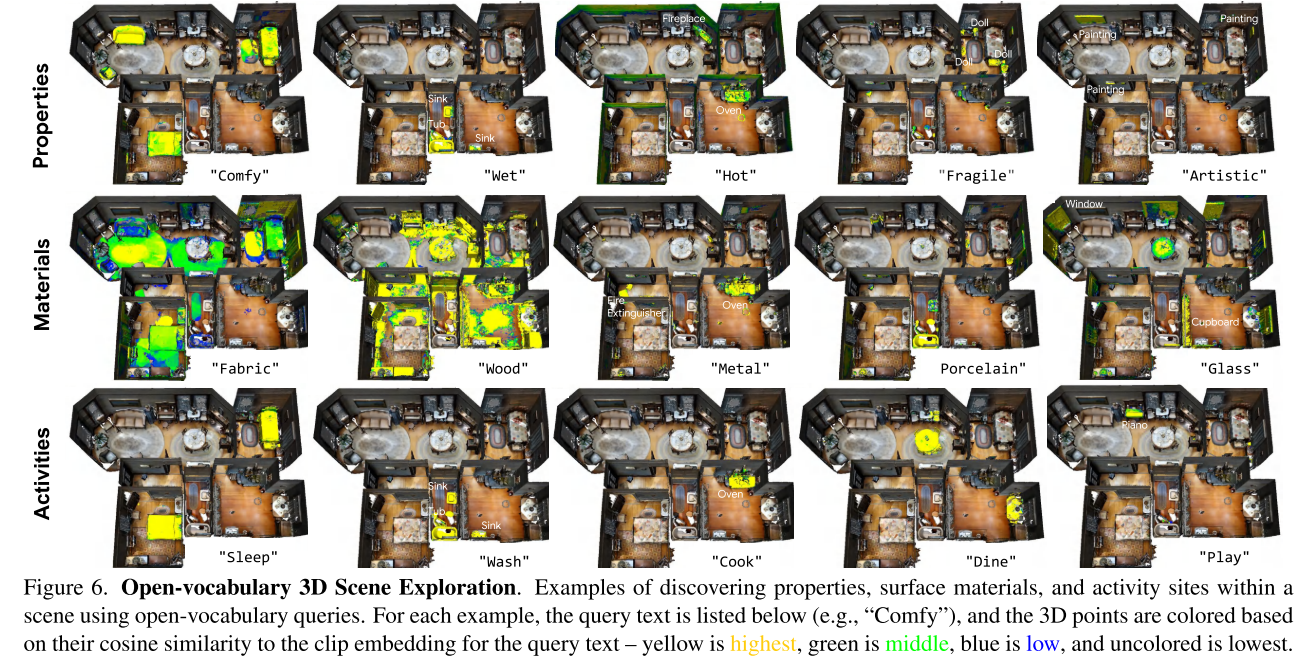
Applications
Open-vocabulary 3D object search
query是文本
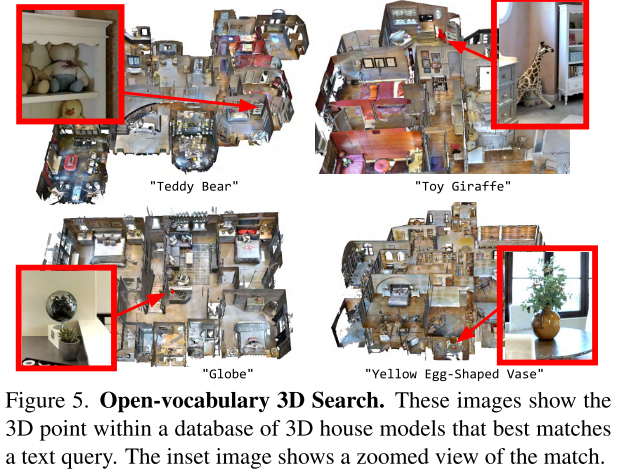
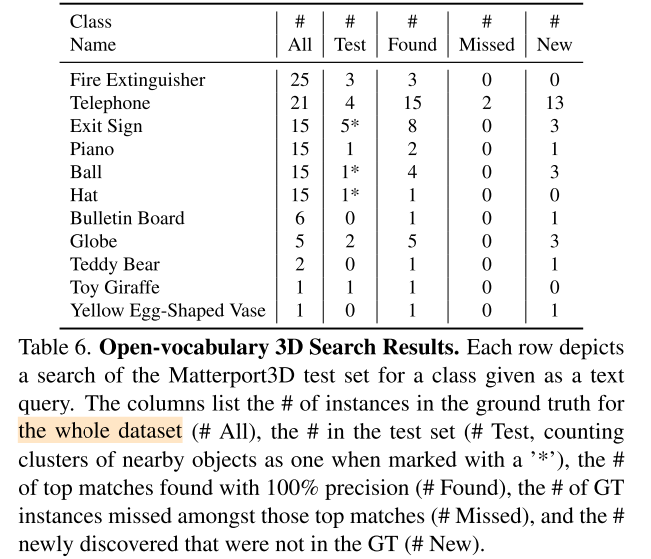
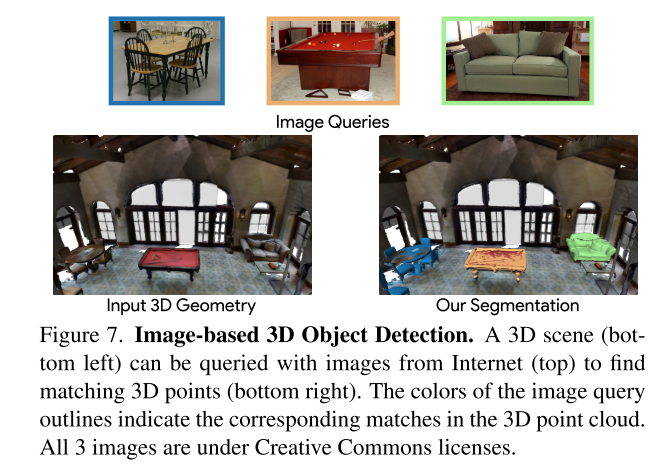
Image-based 3D object detection
query是image
Open-vocabulary 3D scene understanding and exploration
