OVDiff
Diffusion Models for Zero-Shot Open-Vocabulary Segmentation
- text-conditioned image generative models对可能图像的分布进行编码,这提供了一种处理类内变化并捕获文本描述中的模糊性的方法
- text-conditioned image generative models不仅编码对象的视觉外观,而且还提供上下文先验,如背景,这可以大大提高分割质量。
Methodology
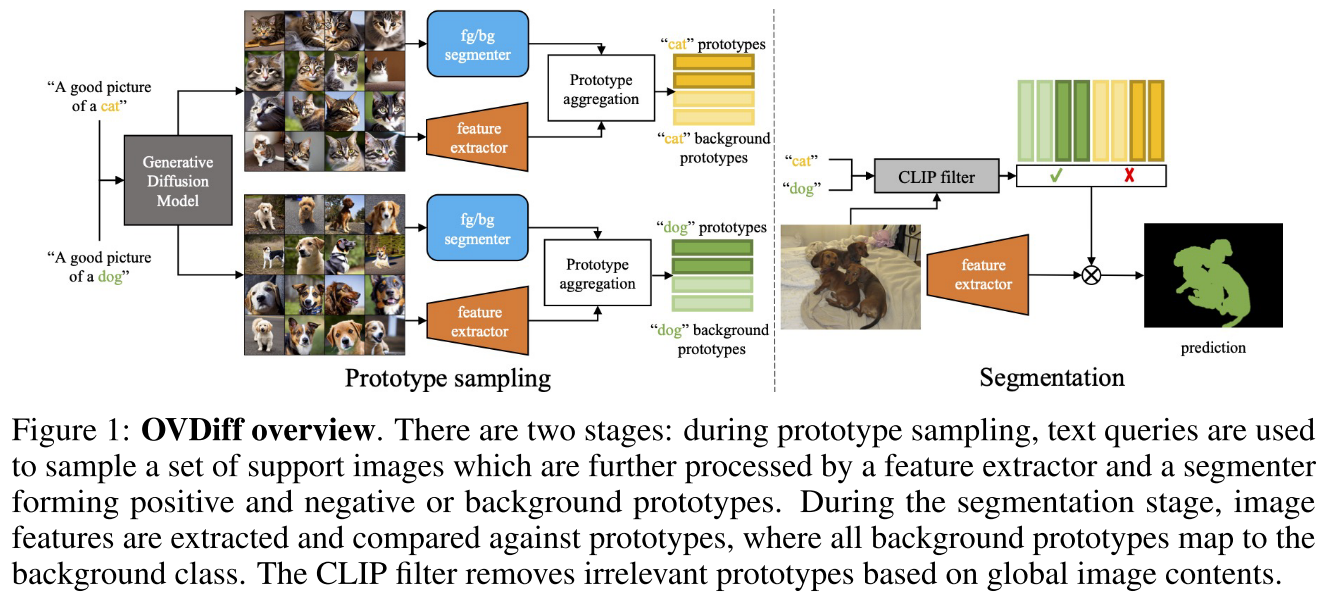
Support set generation
- 基于prompt “A good photo of a $⟨c_i⟩$”使用stable diffusion生成N张support images
Class prototypes
为每个类别生成positive和negative两类prototypes
- Positive prototypes代表图像中与对应类别相关的区域特征
- Negative prototypes代表background区域特征
找与类别$c_i$最相关的区域
- 作者的观察:生成图像的布局在很大程度上依赖于扩散模型的交叉注意图,即pixels attend more strongly to words which describe them
- 基于这个观察,作者直接对cross-attention map所有层、头和去噪步骤求和,得到N张support images对应的N张attribution maps(代表了类别相关的区域)
- 直接对激活图进行阈值分割会导致模糊的分割,因此作者使用CutLER进行无监督实例分割,获得高质量的obejct proposals
- 计算每个mask proposal的attribution平均得分,最高的作为前景,最低的作为背景
- 然后通过现成的预训练特征提取器获得密集图像特征,并计算前景/背景掩码内的平均特征作为prototype,即instance-level prototypes(从每个图像单独计算,且支持集中的每个图像可以被视为类Ci的实例。)
- class-level prototypes则是通过对instance-level prototypes加权求和得到,根据mask size来设置权值
- 通过对foreground and background regions分别进行K-means聚类得到part-level prototypes
Open-vocabulary segmentation
简单地通过每个像素的图像特征与prototype的余弦相似性的来获得,选择在其原型集中具有最高相似度的类
Category pre-filtering
“Stuff” filtering
使用ChatGPT来筛选“thing” or “stuff”(如sky)
Experiment
To generate our support set, we use the Stable Diffusion model v1.5. We set the size of the support set to N = 64, which translates to 4 batches of 16 images samples in parallel on a single A40(48G).
We estimate the total compute used for the experiments in this paper at 190 GPU hours