VLN survey
- What is an intelligent Embodied AI?
- Understand information from Vision,Text,Audio, etc.
- Make the correct action in the environment.
- What can we do to build it from Machine Learning perspective?
- Benchmark:
- Environment as real as possible.
- Communication like human.
- Methods:
- Connecting advancement within single modality.
- Specific solution.
- Training sources.
- Benchmark:
两大难题: 数据稀缺和模型的泛化性低
Definition
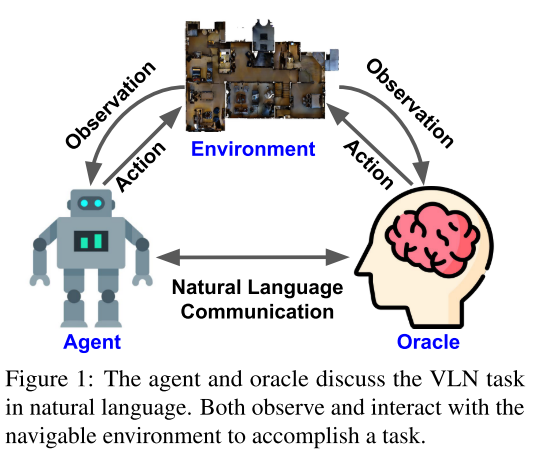
Key elements: Environment, Agent, Oracle(Human)
Environment
Photorealistic
3D
Navigable
Interaction between Agent and Environment
- Environment renders new observation after each action.
- Agent navigate in the environment, with possible object manipulation.
- Communication between Oracle and Agent
- Use Natural Language
- Task Instruction
- Dialog ability
agent和oracle使用自然语言进行交流,智能体可以请求引导,oracle可以做出响应回答。agent根据接收到的指令和观察到的环境进行导航并与环境交互以完成任务,同时oracle观察环境和agent的状态,并可以与通过与环境交互的方式来帮助agent。
Datasets
在视觉语言导航的设定中, MatterPort3D 模拟器是将场景划分为离散的可导航位置点集. 这一做法简化导航过程为一个无向图的探索过程, 即每步移动都从邻近的有限点集中选择下一个目标节点. 这在一定程度上减少了视觉信息对任务的影响。
但高级动作空间中存在过度依赖已知的路径拓扑结构的问题, 不利于未来部署在现实场景中。
受Matterport3D 模拟器不能支持低级动作的影响, 需要通过特定算法将高级动作(节点间的跳转)转换为低级动作(6种基础动作向上、向下、左转 30 度、右转 30 度、前进和停止), 因此很多模型不便于直接由模拟环境转移现实场景中.
Habitat和iGibson支持连续环境
Beyond the nav-graph: Vision-and-language navigation in continuous environments
Topological planning with transformers for vision-and-language navigation
不同数据集从不同角度来解决VLN问题:
- Action Type: Navigation或Navigation+环境交互
- Communication Type: 只要求agent听懂指令 or 听懂指令还要能交流对话,如遇到难以判断的情况向oracle提问
- Environment Type: 室内 or 室外 or 不同地点····
下表是对VLN benchmark的一个总结,从语言复杂度和任务目标(任务复杂度)两个角度对现有的benchmark(17-22)进行了分类。
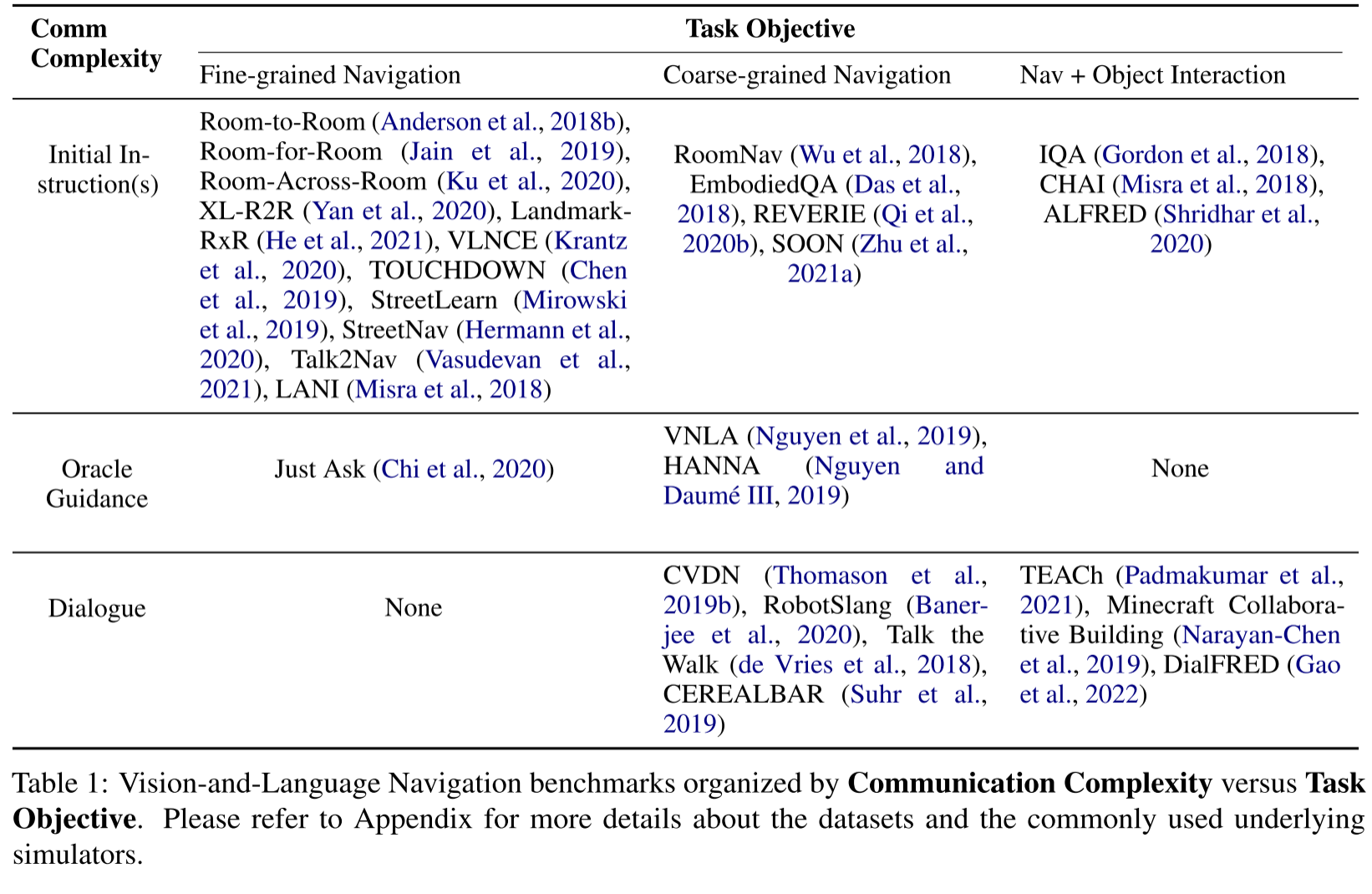
- Communication Complexity(语言复杂度)的3种类型
- 大部分的benchmark集中在Initial Instruction,也就是在初始时给一个指令,这类benchmark构建和效果评估都相对简单

Task Objective(任务复杂度)

Datasets Highlights
Room-to-Room
室内场景,有详细的指令
- The paper that proposes VLN
- Given a detailed instruction, the agent navigates indoors
- It is extended to many other datasets
TOUCHDOWN
基于Google Street View,室外场景
- Outdoor Navigation
- More complex environments than Indoors.
REVERIE
Remote embodied visual referring expression in real indoor environments,第一个粗粒度导航的数据集,没有给出具体的信息,agent会随机初始化在房间里的某一位置,然后给出要找的目标(简洁的指令给出),不会给出具体的路线,因此agent需要有更强的对环境的理解能力,甚至需要一些prior knowledge,比如卧室的大致位置,要找刀-刀一般在厨房,这类先验知识
- Finding a remote goal based on a concise instruction
ALFRED
第一个结合navigation和interaction的数据集,为了完成任务需要和环境交互,比如要去抽屉里拿剪刀,需要先打开抽屉
- In order to achieve the task, the agent need to interact with the
environment
- In order to achieve the task, the agent need to interact with the
VNLA & HANNA
在agent不知道怎么走的时候,向oracle发送求助信号,oracle是知道地图信息的,因此可以给出提示
- Agent sent “help” signal and receive response from Oracle
CVDN
第一个dialogue类型的VLN数据集,需要agent主动提问
- Agent ask question in Natural Language
TEACh
最复杂的数据集之一,要求agent能主动问问题,同时要求navigation和interaction,任务更复杂,对话形式更接近人类对话形式(free-form)
- Free-form dialog
- Navigation & Interaction
SimBot Challenge
基于TEACh
- Build Robot that talks to accomplish task
- Evaluate by human expert
Methods
输入text, vision和action,输出下一个action
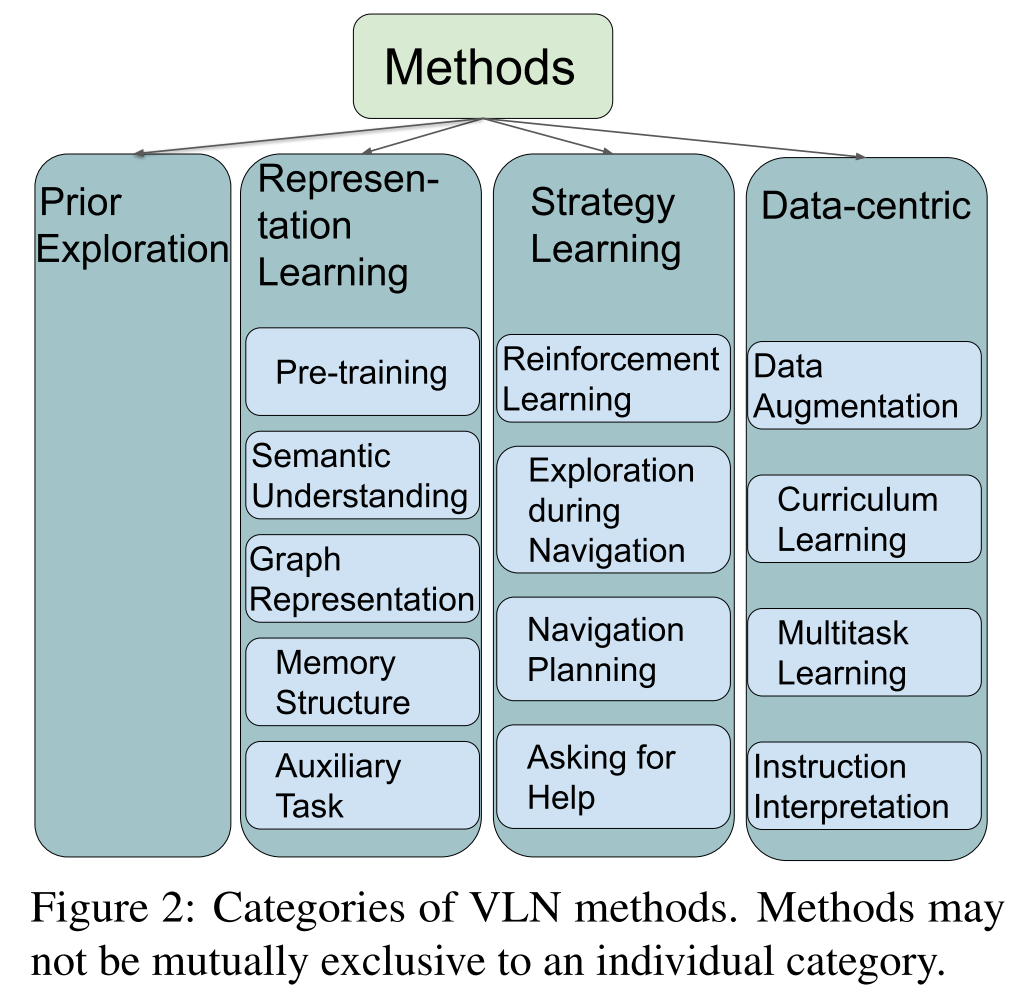
Representation Learning
帮助agent更好的理解环境,引入先验知识
Pre-training
对模型进行预训练,可以直接引入现有的单模态/多模态大模型
- Single modality
- Multi-modality
- VLN domain,在VLN的数据集上做pre-training,如VLN-BERT
Semantic Understanding
相当于加入了人的先验,提供一些landmark去指导agent
- 单模态内重点信息的提取,比如从指令中提取关键词来指导agent
- 模态之间的交互
Graph Representation
- 使用GNN等方式来对图结构进行编码
- 使用Graph来表示地图
Memory Structure
- handling the image history, action history, and dialog history
- HAMT
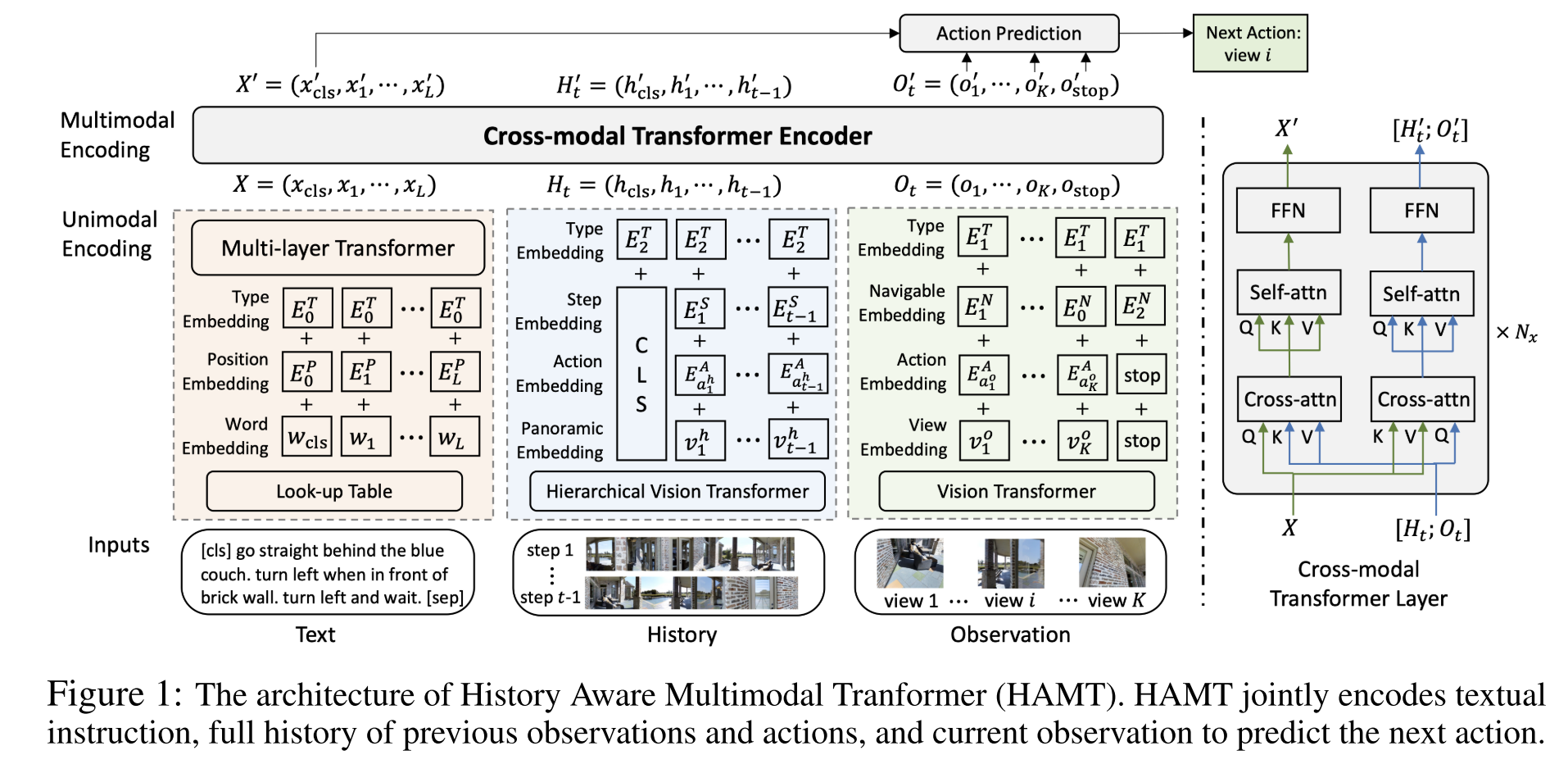
Auxiliary Task
- Using extra loss to 1) get familiar with the environments 2) understand current task
- AuxRN
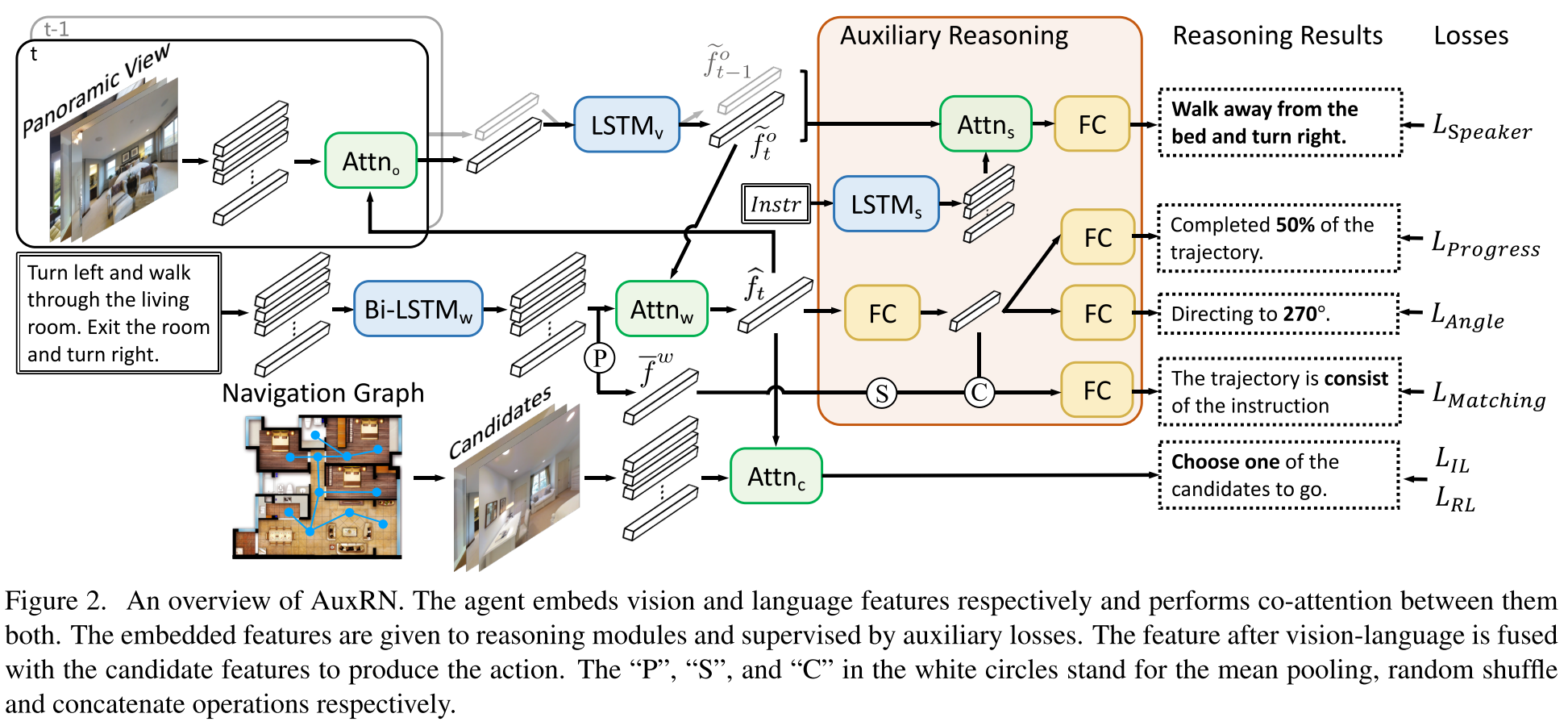
Action Strategy Learning
Reinforcement Learning
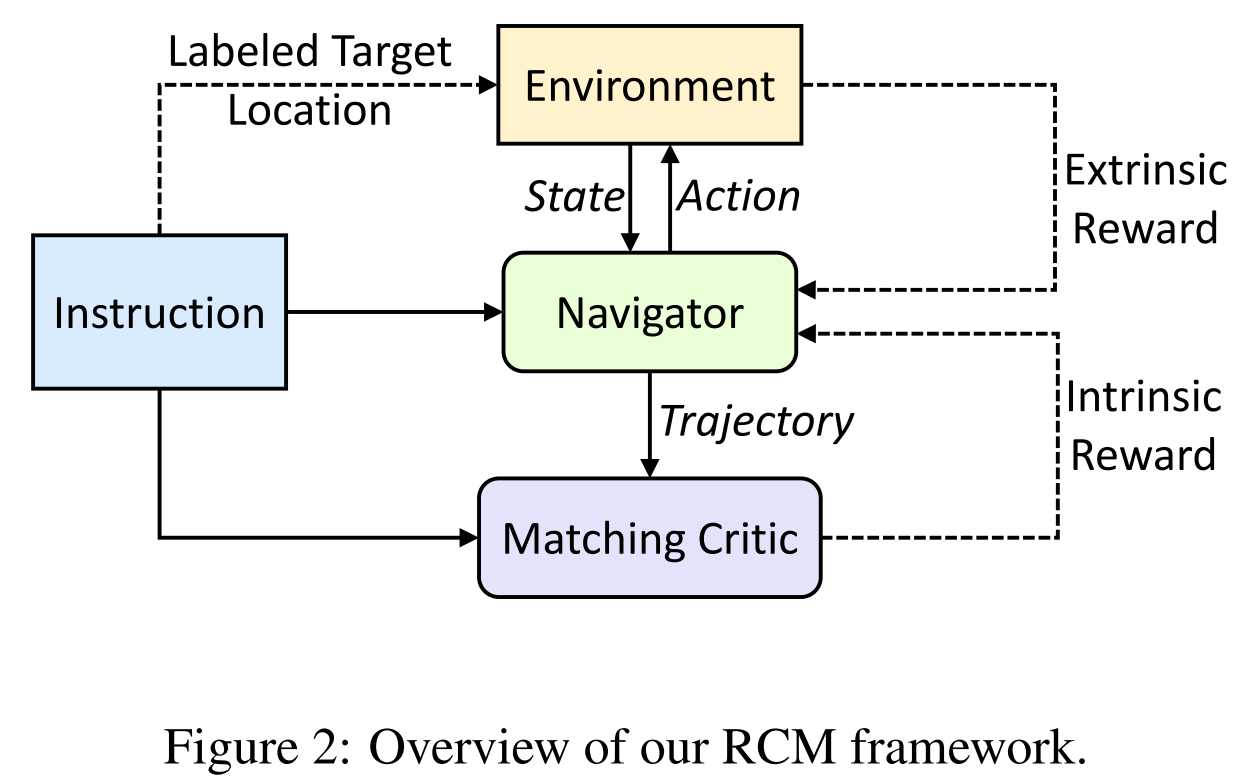
- RCM: connecting reinforcement learning with imitation learning, intrinsic就是使用metric来给reward,extrinsic reward就是使用训练好的model来给reward
- Reward definition
- Evaluation Metrics and proposed criteria
- Rewards from a trained model
Exploration during Navigation
- Student forcing rather than teacher forcing(会随机探索,而不是在一开始就按照数据集定义的动作走)
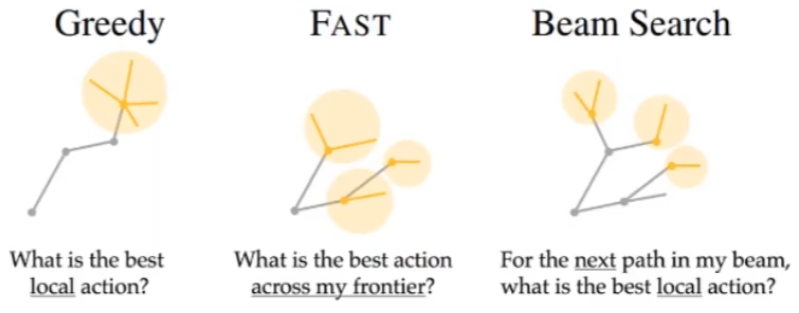
- Explore and even predict different directions(使用网络预测往某个方向走会发生什么,Pathdreamer)
Navigation Planning
提前计划后面的移动方式
- Vision side: waypoint(找出画面中一定要经过的点,做一个先后顺序计划), generating future view, when to stop
- Text side: key objects in instruction, generative methods based on instruction
Asking for Help
- When to ask for help: using action probability, with a specific model
- How to generate questions
Data-centric Learning
Data Augmentation
Trajectory-Instruction Augmentation
生成更多的路径(指令语言)
- speaker-follower model,speark用于生成数据进行augmentation,对随机走的路径生成语言描述,获取新的data pairs
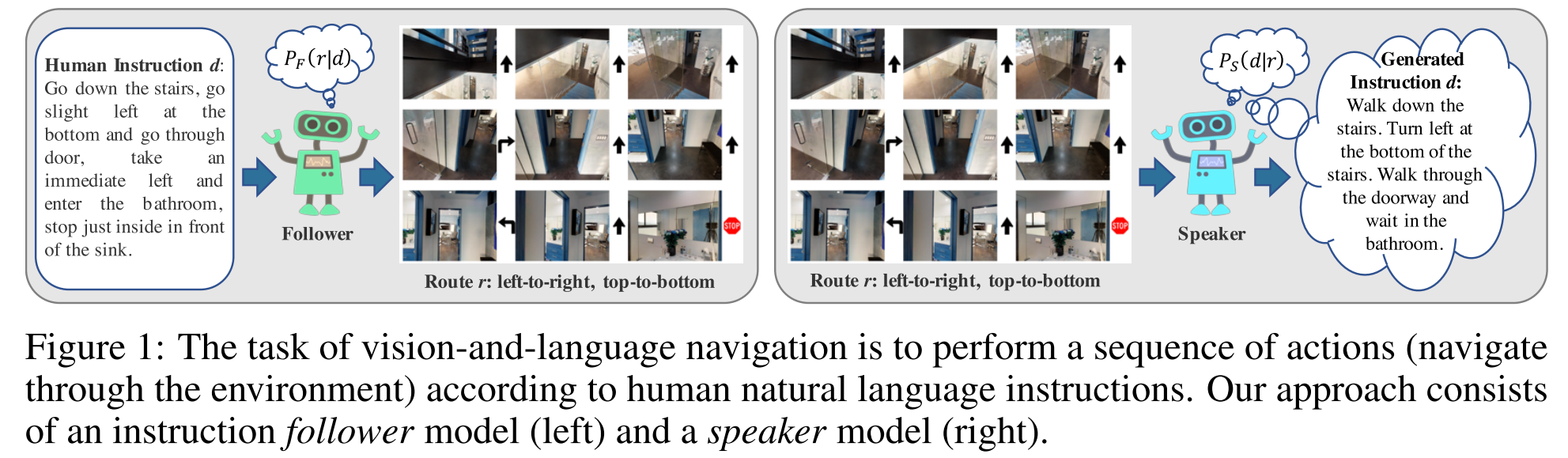
- Augmentation quality control
Environment Augmentation: env drop, env mix
Curriculum Learning
- 从简单的任务开始做,从简单到困难。Room Counts利用路径中包含的room个数来判断难易,instruction lengths则是通过指令长短来判断
Multitask Learning
- 使用不同的VLN任务同时学习
Instruction Interpretation
换一个角度解释指令
- Break the long instruction into short ones
- Using waypoint in the instruction
- Encode several instructions for the same trajectory
Prior exploration
在测试环境中进行探索,自动给出一些label
- Different setting: explore the environments before task execution
- Not comparable to models without prior exploration
Evaluation
Main Metrics in VLN tasks
Goal-oriented Metrics
- Success Rate (SR),任务是否成果,成功为1,不成功为0,统计成功率
- Goal Progress (GP),测量到目标的剩余距离的减少
- Path Length (PL),路径长短
- Success weighted by Path Length (SPL)
Path-fidelity Metrics
路径保真度,要求走出的路径和GT的路径要尽可能相似
- Coverage weighted by LS (CLS)
- Normalized Dynamic Time Warping (nDTW)
- Success weighted by normalized Dynamic Time Warping (SDTW)
Future Work
- 缺乏世界知识
- 如何表示知识
- 需要哪些知识
- 如何将知识和navigation融合在一起
- 如何解决泛化性差的问题
- 引入更多环境的datasets
- 引入更多语言(比如中文下的navigation)
- VLN的最后一步
- 如何和环境实现交互
- 考虑利用LLM来将任务拆分为元操作库里的动作
- 可合作的VLN
- Multiple agents, agent and human
- Simulation to Reality
- Rough Localization(移动的误差)
- Oracle Navigation
- Physical Nature
- Ethics & Privacy
- 连续环境的VLN