TPAMI2022 WSSS/WSIS综述
A Survey on Label-efficient Deep Segmentation: Bridging the Gap between Weak Supervision and Dense Prediction
语义分割 semantic segmentation
实例分割 instance segmentation
全景分割 panoptic segmentation
bridging the gap between weak supervision and dense prediction
引入启发式先验(Unsupervised & image-level supervision)
cross-label constraint
- cross-label constraint:弱标签和密集标签之间存在自然约束,例如图像级类别标签表示至少有一个像素的标签应与该图像级类别标签相同
- Seed area refinement
- Expanding by ensemble:通过不同的CAM集合来扩展种子区域
- Re-finding by erasing
- Discovering by optimization:鼓励分类模型在优化过程中看到更大的区域来发现种子区域
- Reasoning by decoupling:CAM 可能与非目标类的区域重叠的原因可能是存在所谓的共现类,例如“马”和“人”经常同时出现。共现类误导了分类模型。
- causal inference因果推理,分析并解耦了图像与混杂集(即共现类集)之间的因果关系,以防止种子区域被解释为冗余区域。
- copy-paste:将前景图像粘贴到不同的图像上,从而使前景图像中的类与相应背景之间没有刻板的上下文关系,从而鼓励种子区域更多地关注前景区域
- Seed area refinement
cross-pixel similarity
cross-pixel similarity:具有高度相似线索的像素,例如颜色、亮度和纹理,可能属于图像中的同一语义区域;
无监督语义分割
- SegSort
Seed area refinement,使用擦除的方式可能会误导种子区域逐渐扩展到语义不正确的区域。一些方法利用了跨像素相似度的先验来指导种子区域的扩展。
自擦除网络SeeNet,使用显著性图来指导种子区域细化
跨任务
ICCV2021 Leveraging auxiliary tasks with affinity learning for weakly supervised semantic segmentation
Pseudo mask generation
Affinity learning with low-level cues.
ECCV2016 Seed, expand and constrain: Three principles for weakly-supervised image segmentation.
- 仅使用具有高置信度的伪标签进行训练
- 更新的伪标签应与给定的图像级标签一致
- 约束更新的伪掩码符合对象边界
- RRM
Affinity learning with high-level learned features.
- AffinityNet
- IAL
- MM2021 Adaptive affinity loss and erroneous pseudo-label refinement for weakly supervised semantic segmentation
cross-view consistency
cross-view consistency:指同一对象在不同视图中表现出的一致性
无监督语义分割
- 像素级对比学习View-Agnostic Dense Representation (VADeR)
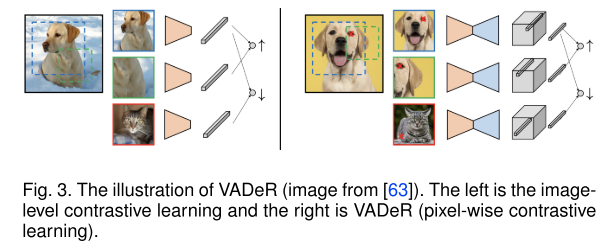
- MaskContrast,结合了 SegSort和对比学习
- 孪生结构Siamese structure
- IIC
- PiCIE(Pixel-level feature Clustering using Invariance and Equivariance)
Seed area refinement, 使用跨视图一致性来提高种子区域的质量,因为跨视图一致性可以促进从同一图像的不同空间扰动获得的 CAM 之间的语义一致性
- SEAM设计了Siamese network,两个分支使用不同的数据增强方式,其中一个分支使用了额外的仿射变换,然后鼓励两分支计算出的CAMs具有一致性
cross-image relation
cross-image relation:来自不同图像的同一类别对象的像素具有语义关系,以从弱标签生成伪密集监督pseudo dense supervision。
无监督语义分割
- Cross-image Relation as Dense Self-supervision:利用无监督预训练的特征作为建立跨图像关系的基础,并进行refine。
NIPS2021 Looking beyond single images for contrastive semantic segmentation learning
提出了一种逐像素对比学习方法,隐式引入了跨图像关系来处理无监督语义分割任务。利用无监督预训练得到的特征进行聚类,然后为每个类分配伪标签,伪标签被用于在对比学习时选择正负对
ICLR2021 Unsupervised semantic segmentation by distilling feature correspondences
STEGO 根据特征显示挖掘了跨图像关系
Seed area refinement,通过鼓励语义共现的不同图像之间的像素级交互来增强种子区域生成的鲁棒性
- co-attention
- GNN
Pseudo mask generation
CIAN 利用跨图像关系学习亲和力,从语义共现的图像对生成伪掩码。在每对图像中,一张图像作为查询图像,另一张作为参考图像。查询图像的特征图由参考图像的特征图根据它们两者之间的逐像素亲和力进行调整,从而产生更完整和准确的伪掩模
AAAI2020 Cian: Cross-image affinity net for weakly supervised semantic segmentation
Segmentation with image-level Supervision
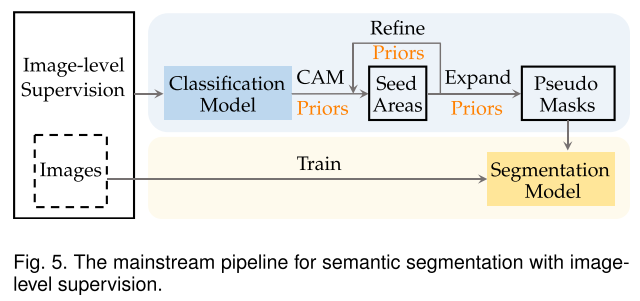
WSSS with image-level supervision 两阶段pipeline
第一阶段产生带噪声的伪掩码(生成高质量的种子区域),第二阶段可以等价于带噪监督的语义分割问题,将伪掩码区域的语义传播到整个图像
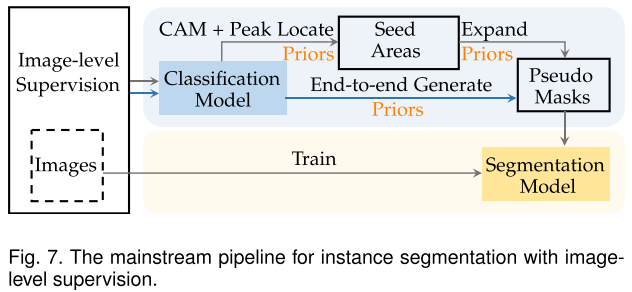
WSIS with image-level supervision 主流pipeline
Instance-level seed area generation
PRM:实例级的种子区域可以通过峰值定位从类别级种子区域获得。由特定类的分类模型提供的种子区域中的高置信度响应(峰值)暗示了属于该类的实例的可能位置。
CVPR2018 Weakly supervised instance segmentation using class peak response
Instance-level pseudo mask generation
Expounding by self-training
PRM的后续工作WISE 和 IAM
BMVC2019 Where are the masks: Instance segmentation with image-level supervision
CVPR2019 Learning instance activation maps for weakly supervised instance segmentation
IRNet
Generating by end-to-end training
Label-PEnet,使用cross-label constraint先验,以在线和粗到细的方式将图像级标签转换为像素级标签,设计了一个由四个并行模块组成的级联管道,即分类、对象检测、实例细化和实例分割模块。采用课程学习策略进行训练,该策略将标签从图像级监督推广到像素级伪掩模,并逐渐提高准确性。
ICCV2019 Label-penet: Sequential label propagation and enhancement networks for weakly
supervised instance segmentationWSIS-CL,结合了OICR
WACV2021 Weakly supervised instance segmentation by deep community learning
PDSL,并行执行弱监督对象检测和自监督实例分割。这两个分支的结果受到相关学习的约束,以保持一致的预测
ICCV2021 Parallel detection-and-segmentation learning for weakly supervised instance segmentation
Segmentation with Box-level Supervision
narrow down the search space
Semantic segmentation with box-level supervision
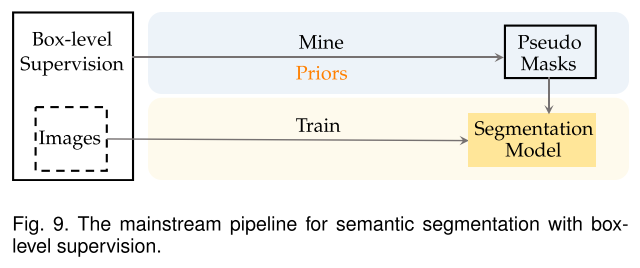
使用Box-level Supervision进行语义分割的核心挑战转变为区分带注释的边界框内的前景对象和背景区域
Boxsup交替更新伪掩码和分割模型,使用unsupervised region proposal method (MCG,Multiscale combinatorial grouping,CVPR2014)来提出建议区域,然后重复执行以下步骤:
使用分割模型为每个候选分割(candidate segment)预测语义标签
对于每个annotated bounding box,从预测为与边界框相同的语义标签的候选分割中,选择重叠区域最大的一个作为边界框的伪掩码
使用伪掩码更新分割模型
但本方法中使用的MCG并未考虑Box-level supervision,因此伪掩码的可靠性不高。
Boxsup: Exploiting bounding boxes to supervise convolutional networks for semantic segmentation,ICCV 2015
计算注释边界框中每个类的填充率filling rate,指导分割模型训练
Box-driven class-wise region masking and filling rate guided loss for weakly supervised semantic segmentation, CVPR2019
计算填充率based on CAM-like map,减少在背景区域的兴趣
Box2seg: Attention weighted loss and discriminative feature learning for weakly supervised segmentation, ECCV2020
通过从带注释的边界框中删除背景区域来获得伪掩码。作者假设图像背景区域中的small patches在感知上是一致的,这为删除每个带注释的边界框内的背景像素提供了标准
Background-aware pooling and noise-aware loss for weakly-supervised semantic segmentation,CVPR2021
Instance segmentation with box-level supervision
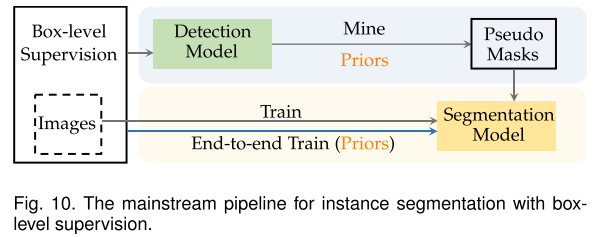
Mask prediction by self-training
SDI使用整个标注框区域或框内Grabcut产生的初始分割作为伪掩码,然后进行self-training来迭代细化伪掩码并最终产生预测掩码
Simple does it: Weakly supervised instance and semantic segmentation, CVPR 2017
BBAM使用来自object detector的高级语义信息来产生伪掩码。作者试图在bounding box中找到一些可学习的区域,object detector可以从中预测与从整个bounding box区域获得的结果几乎相同的检测和分类结果。直观地,这些区域代表对象的判别部分。The areas of different object proposals corresponding to a given annotated box were combined as its pseudo mask
Bbam: Bounding box attribution map for weakly supervised semantic and instance segmentation, CVPR 2021
BoxCaSeg 通过从显着分割数据集引入额外的知识来增强前景/背景分离的能力,从而获得更精确的伪掩码
Weakly-supervised instance segmentation via class-agnostic learning with salient images, CVPR 2021
Mask prediction by end-to-end training
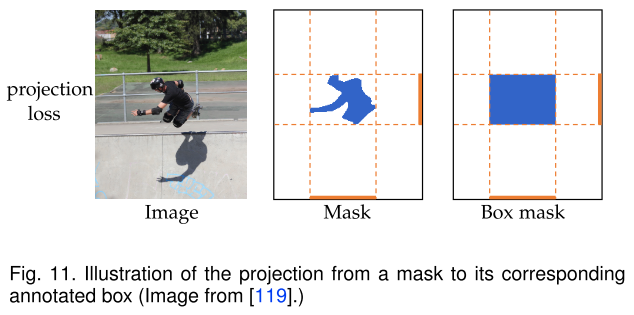
BBTP和BoxInst使用框监督的端到端实例分割,设计了projection loss来完成cross-label constraint.投影损失保证了给定的标注框与预测的mask沿其四侧的投影之间的一致性。尽管如此,这种投影损失不能对预测掩模的形状施加任何约束,这可能导致出现无意义的掩码,例如全矩形。为了解决这个问题,BBTP和Boxinst中还提供了额外的成对损失函数,它们分别基于空间位置和颜色定义了cross-pixel similarity。
Weakly supervised instance segmentation using the bounding box tightness prior, NIPS 2019
Boxinst: High-performance instance segmentation with box annotations, CVPR 2021
Semi-supervised Segmentation
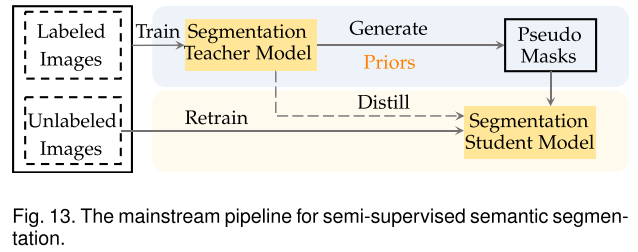
Semi-supervised semantic segmentation
仅提供了一小部分训练图像的像素级标注,而其余训练图像则没有标注。半监督语义分割的目标是将大量未标记的训练图像纳入训练以提高分割性能。一种常用的半监督语义分割的框架是图所示的self-training,它将在带标签的训练图像上训练的分割模型 (教师模型) 应用于无标签的训练图像,以生成伪密集标签 (mask),然后用伪密集标签 重新训练分割模型(学生模型)。
Semantic segmentation from noisy supervision
- 作者观察到一种现象,即随着训练的进行,分割模型倾向于记住注释中的错误。为了防止对错误的过度拟合,他们设计了一种自适应的早期停止机制,并利用多尺度cross-view consistency,来增强对错误标注的鲁棒性。
Adaptive early-learning correction for segmentation from noisy annotations,CVPR 2022
- 提出通过不确定性估计发现噪声标签,根据cross-view consistency计算不同尺度下预测图之间的像素方差来实现
Uncertainty estimation via response scaling for pseudo-mask noise mitigation in weakly-supervised semantic segmentation, AAAI 2022
噪声标签:What uncertainties do we need in bayesian deep learning for computer vision? NIPS 2017